In an era of dwindling glaciers, Southern Patagonia has managed to hold on to a surprising amount of its ice. But, A new study in Scientific Reports from INSTAAR postdoc Matthias Troch suggests that this protective effect might be pushed up against its limits soon.
Before making predictions, Troch and his collaborators looked back in time. They used an equation that, when plugged into NASA’s ice-sheet and sea-level system model, simulated glacial dynamics for the past six millenia. The results showed that precipitation, not temperature, was the main culprit of glacier fluctuation during around 4,500, of the past 6,000 years, or 76 percent of the time. In more recent years, increased snowfall protected the glaciers from rising global temperatures.
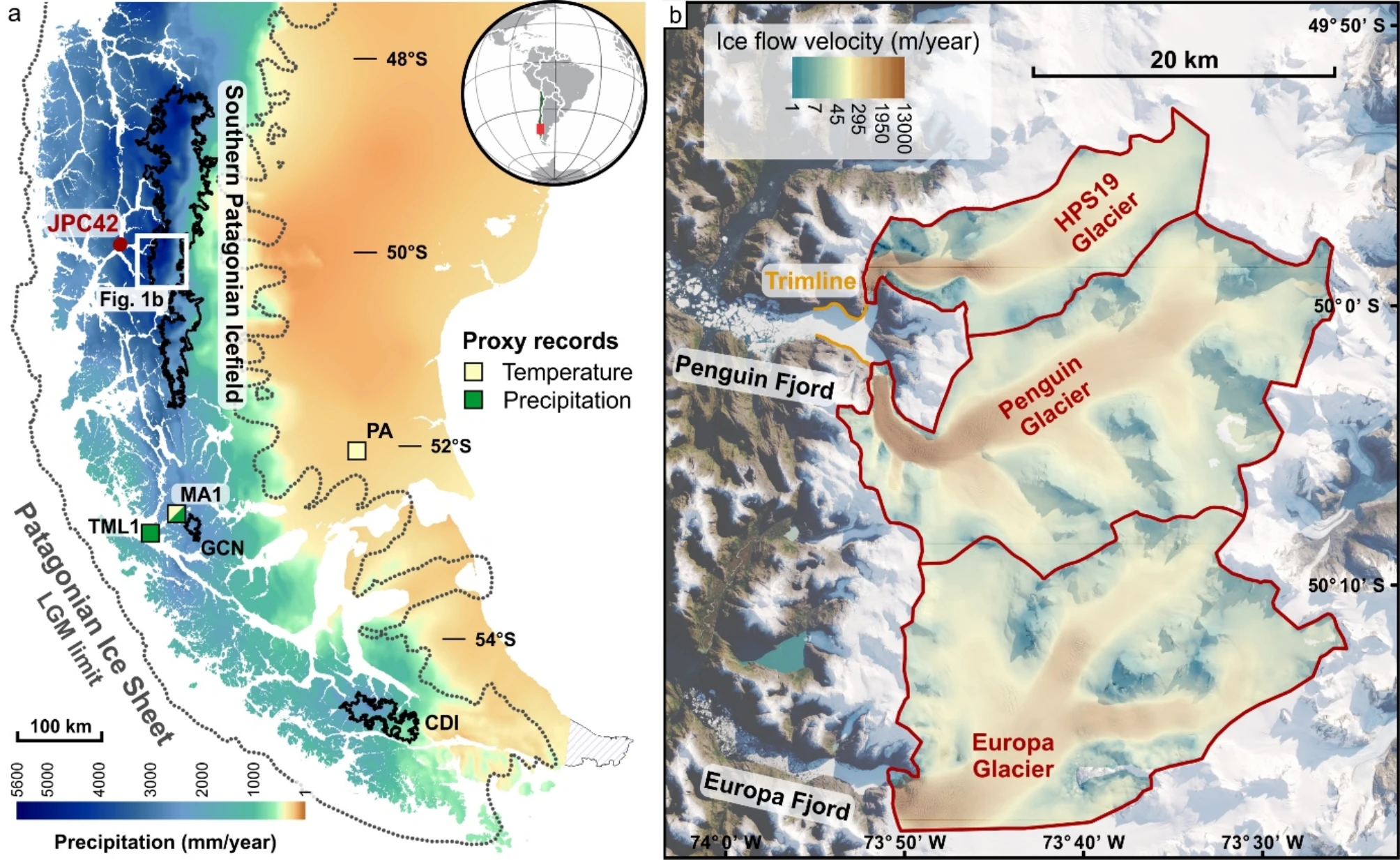
These simulations were hyper-focused. The researchers singled out three connected glaciers on the wetter, ocean-facing side of the Patagonia range in Southern Chile. The region came with a distinct scientific advantage. In 2005, a team aboard the American research vessel Nathaniel B. Palmer collected a sediment core from a nearby fjord. Troch and his collaborators got their hands on the sediment core and used it to validate and refine their model. In essence, they had a physical piece of evidence to provide proof that they were on the right track.
Once they had reconciled the numerical model with the sediment core, the researchers began to ask questions about the future. In particular, they were interested in what would happen to the glaciers under different emissions scenarios. If humanity stopped burning fossil fuels today, would the glaciers remain protected? What if we continued to increase our greenhouse gas emissions?
Troch and his colleagues found that increased snowfall would continue to protect the glaciers from melt if regional warming was curbed at 1.5 degrees celsius above turn-of-the-century levels. This benchmark is attainable. Yet, to limit warming to this level, humanity would need to rapidly decarbonize — temperatures are on track to climb to 2.8 degrees celsius in patagonia by the end of the century if current emissions persist.
“The study underscores the need for deep emission cuts to protect glaciers, which is vital to limit global sea-level rise,” Troch said.
The researchers also modeled what would happen if we didn’t cut back, and the outlook was not so sunny. A warmer, wetter climate could lead to rapid melt.
“This could push glaciers into a new regime dominated by rain rather than snowfall,” Troch explained.
Troch hopes that research like his will bolster the global call-to-action for green policies and practices. While news about the climate is often gloomy, there are still many harms that can be prevented if humanity strives for sustainability.
“If we can limit emissions there is hope for protecting maritime glaciers,” Troch said.
Troch also hopes that the study will catalyze further research into maritime glaciers around the world. The conclusions drawn in Southern Patagonia might be replicated in Norway, Alaska, Iceland or New Zealand. The only way to find out is further research.
